After we ask B2B clients in regards to the causes they select the manufacturers they work with, we hear related themes crop up throughout varied sectors: value, service, and product availability, to call only a few. We additionally hear related themes raised as ache factors associated to working with chosen manufacturers.
B2B decision-making on manufacturers is a steadiness of a variety of various elements. Whereas clients could understand the value provided by one model to be excessive, wonderful advantages and its industry-leading expertise providing can justify what they’re requested to pay. Equally, clients could select to forfeit added-value advantages provided by extra premium suppliers, like further coaching or sources, if the value level of one other model with a much less subtle providing is simply too aggressive to miss.
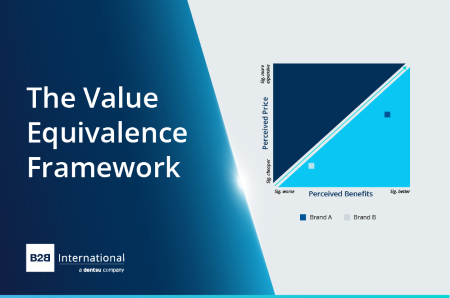
The Worth Equivalence Framework
To guage the notion of manufacturers inside this ecosystem of various decision-making elements, we frequently use a easy questioning method that asks analysis respondents to assume in relative phrases. This method is known as the worth equivalence framework and consists of two quite simple questions:
-
How would you price [BRAND]’s advantages versus different related manufacturers? Answered utilizing a 5-point score scale from ‘Considerably higher’ to ‘Considerably worse’
-
How would you price [BRAND]’s value versus different related manufacturers? Answered utilizing a 5-point score scale from ‘Considerably costlier’ to ‘Considerably cheaper’
The variables in daring aren’t at all times set in stone and could be tweaked to go well with the model in query. For instance, it’s possible you’ll need to measure high quality and value in case your model is extra product-focused (or perhaps a totally different product-focused attribute). That mentioned, it is suggested to incorporate one attribute that’s value or value-related, as this framework focuses on figuring out whether or not a model’s worth is justified by different elements of its supply.
Analyzing the Knowledge
We have a tendency to investigate the suggestions from these two questions collectively, plotting the outcomes on two totally different axes.
Taking the typical rating for each questions for the model that’s being rated, you’re going to get your two information factors to your two axes. This provides you with your plot level to your manufacturers, and it is possible for you to to see how they’re positioned in opposition to one another. As a basic rule, your model needs to be positioned on the correct of the road; manufacturers on the left of the road are extra susceptible to dropping market share primarily based on lack of perceived worth.
To grasp the suggestions right here, take into account the place the manufacturers are positioned. Model A is perceived as a costlier supplier, however its advantages are mentioned to be considerably higher than different manufacturers, so it’s in a cushty place of a justified premium. You may even argue that Model A has scope to extend its premiums additional to get nearer to the worth equivalence line. Against this, Model B is perceived as having worse advantages, however its costs are additionally very low in comparison with others available in the market, so its place is comparatively balanced. You’ll be able to add as many manufacturers as you’ve gotten information for to this chart so you’ll be able to construct an image of the market panorama and see the place your model is positioned on worth equivalence in opposition to different suppliers.
When and The best way to Use the Worth Equivalence Framework
The worth equivalence framework is usually seen in research that contact available on the market panorama a model operates in and is a helpful gauge for understanding the way it’s perceived in opposition to opponents. To do that, you would want to be sure you ask respondents not nearly your main model, but additionally about competitor manufacturers. These must be manufacturers that the respondents use in order that they may give them a good score. You’ll be able to mess around with the outcomes and examine information by segments inside your pattern to see if the perceived worth of manufacturers differs by group.
A closing notice: watch out of any potential bias in your pattern and the way this will likely influence the outcomes. If you’re interviewing your clients who you realize are loyal supporters of your model, don’t be shocked to see yours performing higher than the competitors – a consultant market pattern provides you with a much less biased view of this matter.