What precisely occurred?
Akamai, a number one Content material Supply Community (CDN) supplier strives to assist net customers around the globe entry and show web site content material in essentially the most seamless attainable method.
Akamai achieves this by benefiting from a large community of edge servers (factors of presence or ‘PoPs’) which can be configured to ship content material to customers from the geographically closest server to that consumer, due to this fact boosting the switch velocity. Nevertheless, on July twenty second, their service skilled a disruption, inflicting the web sites of firms that solely depend on Akamai’s companies to go down :
- Within the morning of July twenty second (round 11:30 AM CT), Akamai stated in a tweet that they had been investigating a service disruption.
- At midday (round 1:00 PM CT) Akamai said {that a} software program configuration replace triggered a bug within the DNS system, the system that directs browsers to web sites. This precipitated a disruption impacting availability of some buyer web sites.
- Shortly adopted by a tweet saying that the disruption lasted as much as an hour. Upon rolling again the software program configuration replace, the companies resumed regular operations and Akamai confirms this was not a cyberattack in opposition to Akamai’s platform.
One more outage, time for change?
Within the meantime, that is the third large-scale web outage in two months, and already the second brought on by Akamai.
Earlier this 12 months, in June, tons of of internet sites together with Spotify, Netflix, and Amazon went down for about an hour due to a glitch within the content material supply community Fastly. Ten days later, banks, airways, inventory exchanges and buying and selling platforms skilled brief outages, which in keeping with Akamai was the results of a bug of their service that helps mitigate distributed denial-of-service (or DDoS) assaults.
Massive-scale web site and net app outages occur sometimes and often don’t final very lengthy. Content material supply networks and different internet hosting companies leverage a worldwide community of backup servers designed to restrict the chance of disruptions when issues go down. Nevertheless, when issues go down, and so they do – this will have devastating penalties for web sites’ model identify and income streams.
Outages that came about just lately have precipitated specialists to warn of the dangers of the web’s reliance on a comparatively small variety of core infrastructure suppliers. As said by Nick Merrill, analysis fellow at UC Berkeley’s Middle for Lengthy-Time period Cybersecurity: “CDNs are the most important centralized level on the web, making them a possible goal for cybercriminals or authorities actors. If one in every of them goes down big swaths of the web might go along with it.”
An answer for CDN outages: Multi CDN
As will be seen from this incident, CDN suppliers like Akamai are susceptible to outages, inflicting downtime for all web site homeowners who rely solely on their companies at any time when these companies expertise a glitch.
Web sites must be out there to customers freed from lags and down occasions. Due to this fact, limiting and even higher eliminating the dangers related to outages is extraordinarily essential. That is the place Multi CDN options come into play.
A Multi CDN setup, because the identify implies, is an answer that leverages a number of CDNs from totally different CDN suppliers concurrently to spice up the velocity of content material supply and assists in avoiding outages and latency points.
How Mlytics helped customers to get rid of downtime
Mlytics leverages RUM and artificial monitoring to gather CDN efficiency knowledge together with CDN latency and availability.
These knowledge undergo the Mlytics resolution engine, serving to our customers establish and select the best-performing CDN routinely. These collective options are what we name : Good Load Balancing.
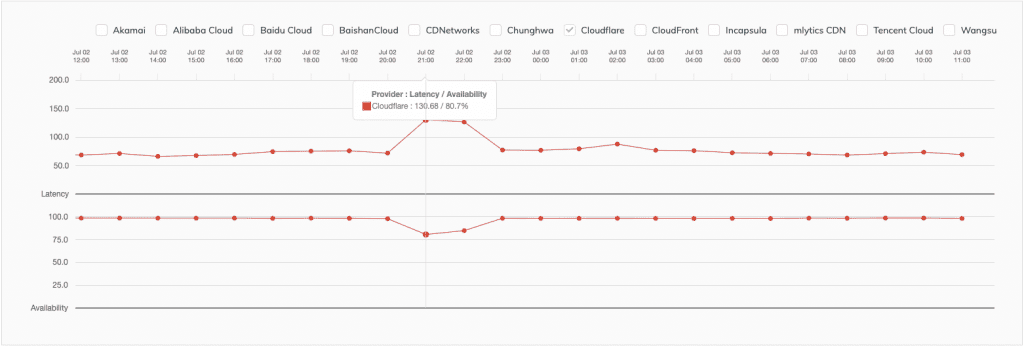
These knowledge are additionally displayed on the ‘Pulse’ (efficiency analytics) chart, which supplies a holistic overview of every CDN’s efficiency at a sure time.
Akamai is among the a number of CDNs accessible by way of the Multi CDN market (Energy-Ups) on the Mlytics platform. When the Akamai outage occurred, Mlytics Good Load Balancing modified Akamai with the following best-performing CDN (totally different for every area) for consumer requests.
This chart exhibits the optimization choices made by our Good Load Balancing answer, it shows which CDNs had been chosen throughout a sure timeframe. As proven, Stackpath and Cloudfront had a number of question spikes because of the Akamai efficiency drop – the system routinely switched Akamai with higher performing CDNs.
This efficiently helped our prospects mitigate Akamai’s outage, and we acquired no complaints over the course.
On the Pulse chart, we additionally see a drop when it comes to availability for Akamai in the identical time-frame. This helps illustrate what occurred when aligning this with the chart above.
Each CDN supplier goals to ship essentially the most seamless consumer expertise attainable, however as seen from latest outages, issues are likely to go haywire. At Mlytics we assist our prospects to get rid of the dangers related to outages and latency to make sure most uptime always.
Lesson discovered, put together for downtime
We must always contemplate the outage brought on by Akamai as a wake-up name, it alerts us that CDN companies do expertise downtime. Whatever the dimension or scale, no one can keep proof against the vulnerabilities of misconfigurations, cyber assaults, or different glitches.
Therefore, it is very important have a stable cloud redundancy and catastrophe restoration plan in place to stop any occasion from inflicting your service to go down. As said by Nick Merril, when a CDN goes down, elements of the web go along with it, and we must always concentrate on the chance of relying solely on a comparatively small variety of core infrastructure suppliers.
Choosing a Multi CDN setup is a proactive strategy that eliminates the necessity for reactive ones later.